A) both structural unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
B) neither structural unemployment nor the natural rate of unemployment.
C) structural unemployment, but not the natural rate of unemployment.
D) the natural rate of unemployment, but not structural unemployment.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Rupert is collecting unemployment insurance benefits. To continue to receive his benefits, he must be looking for work. Because he'd like to continue collecting benefits rather than take a job, he applies at places that are unlikely to hire him. People like Rupert make the reported unemployment rate less than it would otherwise be.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who would be included in the labor force?
A) Louie, who is waiting for his new job to start
B) Daisey, who has become discouraged looking for a job and has quit looking
C) Donald, an unpaid stay-at-home father
D) None of the above is correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Sectoral shifts contribute to structural unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 28-3 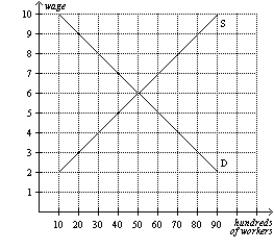 -Refer to Figure 28-3. If the government imposes a minimum wage of $8, then employment will decrease by
-Refer to Figure 28-3. If the government imposes a minimum wage of $8, then employment will decrease by
A) 0 workers.
B) 2,000 workers.
C) 3,000 workers.
D) 4,000 workers.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics produces data on unemployment and other aspects of the labor market from a regular survey of about 60,000 households, called the Current Population Survey.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who of the following are included in the Bureau of Labor Statistics' "employed" category?
A) certain unpaid workers
B) part-time workers
C) workers on vacation
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bureau of Labor Statistics places people in the "employed" category if they
A) are temporarily absent from their jobs.
B) are self-employed.
C) work without pay in a family member's business.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that roofers are not unionized. If roofers unionize, then the supply of labor in other sectors of the economy will
A) decrease, raising wages in industries that are not unionized.
B) decrease, reducing wages in industries that are not unionized.
C) increase, raising wages in industries that are not unionized.
D) increase, reducing wages in industries that are not unionized.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unions
A) and firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker effort both create frictional unemployment.
B) creates frictional unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker effort creates structural unemployment.
C) creates structural unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker effort creates frictional unemployment.
D) and firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker effort both create structural unemployment.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person who is counted as "unemployed" by the Bureau of Labor Statistics
A) is also in the labor force.
B) must have recently looked for work or be on temporary layoff.
C) must be at least 16 years old.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 28-4 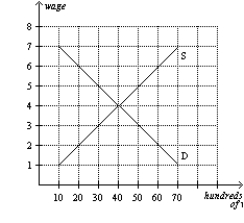 -Refer to Figure 28-4. If 4,000 workers are unemployed, then the minimum wage must be
-Refer to Figure 28-4. If 4,000 workers are unemployed, then the minimum wage must be
A) $2.
B) $4.
C) $5.
D) $6.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the demand for hard-wood flooring increases, while the demand for wall-to-wall carpeting decreases. Based on this change in consumer tastes, the demand for hard-wood-flooring factory workers in North Carolina increases, while the demand for carpet factory workers in Georgia decreases. This is an example of
A) frictional unemployment created by efficiency wages.
B) structural unemployment created by efficiency wages.
C) frictional unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
D) structural unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The labor-force participation rate is computed as
A) (Employed ÷ Adult Population) × 100.
B) (Employed ÷ Labor Force) × 100.
C) (Labor Force ÷ Adult Population) × 100.
D) (Adult Population ÷ Labor Force) × 100.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Table 28-11
2010 Labor Data for Tajnia 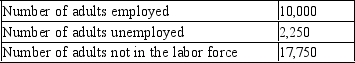 -Refer to Table 28-11. The total adult population of Tajnia in 2010 is 30,000.
-Refer to Table 28-11. The total adult population of Tajnia in 2010 is 30,000.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The deviation of unemployment from its natural rate is called
A) the economic rate of unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) frictional unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount of unemployment varies
A) little over time and across countries.
B) little over time but substantially across countries.
C) substantially over time but little across countries.
D) substantially over time and across countries.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 28-4  -Refer to Figure 28-4. If the government imposes a minimum wage of $2, how many workers will be unemployed?
A) 0
-Refer to Figure 28-4. If the government imposes a minimum wage of $2, how many workers will be unemployed?
A) 0
A) 2,000
B) 4,000
C) 6,000
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an unemployed person quits looking for work, then, eventually the unemployment rate
A) decreases, and the labor-force participation rate is unaffected.
B) and the labor-force participation rate both decrease.
C) is unaffected, and the labor-force participation rate decreases.
D) and the labor-force participation rate are both unaffected.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Table 28-10
The table below lists the number of people by labor force classification for the country of Springfield. 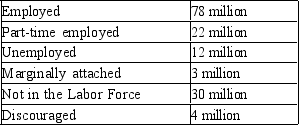 -Refer to Table 28-10. Calculate the U-5 unemployment rate.
-Refer to Table 28-10. Calculate the U-5 unemployment rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 678
Related Exams