A) C.
B) C + B.
C) A + B + D.
D) B + C + D.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the world price of a good is greater than the domestic price in a country that can engage in international trade, then that country becomes an importer of that good.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The small-economy assumption is necessary to analyze the gains and losses from international trade.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a nation first begins to trade with other countries and the nation becomes an exporter of soybeans,
A) this is an indication that the world price of soybeans exceeds the nation's domestic price of soybeans in the absence of trade.
B) this is an indication that the nation has a comparative advantage in producing soybeans.
C) the nation's consumers of soybeans become worse off and the nation's producers of soybeans become better off.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-18. On the diagram below, Q represents the quantity of peaches and P represents the price of peaches. The domestic country is Isoland. 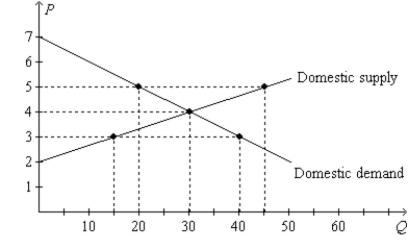 -Refer to Figure 9-18. If Isoland allows international trade and if the world price of peaches is $3, then
-Refer to Figure 9-18. If Isoland allows international trade and if the world price of peaches is $3, then
A) Isoland has a comparative advantage, relative to other countries, in producing peaches.
B) Isoland will export peaches.
C) producer surplus with trade exceeds producer surplus without trade.
D) consumer surplus with trade exceeds consumer surplus without trade.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-5
The figure illustrates the market for tricycles in a country. 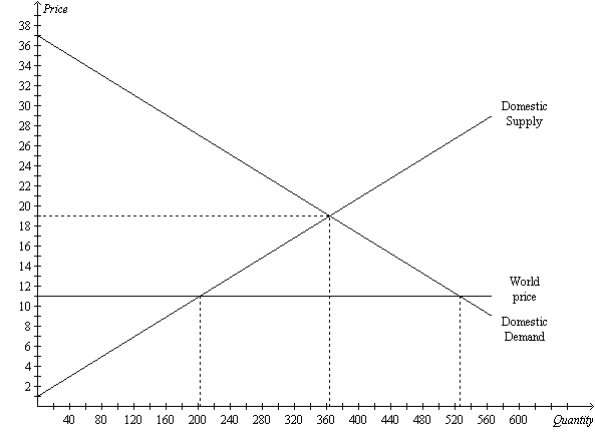 -Refer to Figure 9-5. With trade, total surplus is
-Refer to Figure 9-5. With trade, total surplus is
A) $3,240.
B) $6,480.
C) $7,760.
D) $15,520.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-5
The figure illustrates the market for tricycles in a country.  -Refer to Figure 9-5. With trade, producer surplus is
-Refer to Figure 9-5. With trade, producer surplus is
A) $500.
B) $1,000.
C) $1,500.
D) $2,000.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The world price of a ton of steel is $1,000. Before Russia allowed trade in steel, the price of a ton of steel there was $650. Once Russia allowed trade in steel with other countries, Russia began
A) exporting steel and the price per ton in Russia remained at $650.
B) exporting steel and the price per ton in Russia increased to $1,000.
C) importing steel and the price per ton in Russia remained at $650.
D) importing steel and the price per ton in Russia increased to $1,000.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following tools and concepts is useful in the analysis of international trade?
A) total surplus
B) domestic supply
C) equilibrium price
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
William and Jamal live in the country of Dumexia. When Dumexia legalized international trade in bananas, the price of bananas in Dumexia increased. As a result, William became better off and Jamal became worse off. It follows that William is a seller, and Jamal is a buyer, of bananas.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-15 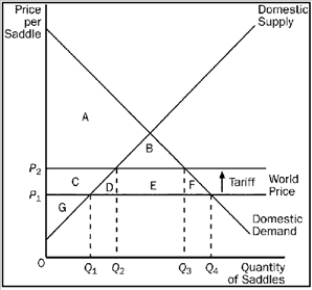 -Refer to Figure 9-15. With the tariff, the quantity of saddles imported is
-Refer to Figure 9-15. With the tariff, the quantity of saddles imported is
A) Q3 - Q1.
B) Q3 - Q2.
C) Q4 - Q1.
D) Q4 - Q2.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since World War II, GATT has been responsible for reducing the average tariff among member countries from about
A) 40 percent to about 5 percent.
B) 40 percent to about 20 percent.
C) 80 percent to about 20 percent.
D) 20 percent to about 10 percent.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-15  -Refer to Figure 9-15. As a result of the tariff, there is a deadweight loss that amounts to
-Refer to Figure 9-15. As a result of the tariff, there is a deadweight loss that amounts to
A) B.
B) E.
C) D + F.
D) B + D + E + F.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-8. On the diagram below, Q represents the quantity of cars and P represents the price of cars. 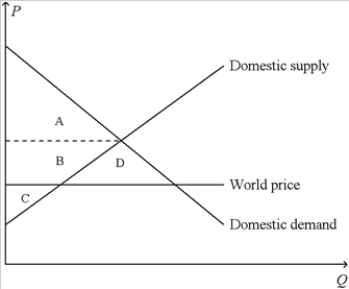 -Refer to Figure 9-8. When the country for which the figure is drawn allows international trade in cars,
-Refer to Figure 9-8. When the country for which the figure is drawn allows international trade in cars,
A) consumer surplus increases by the area B.
B) producer surplus decreases by the area B + D.
C) total surplus increases by the area D.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a government imposes a tariff on a product, the domestic price will equal the world price.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-3. The domestic country is China. 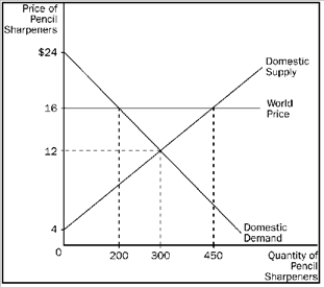 -Refer to Figure 9-3. Relative to a no-trade situation, which of the following comes with trade?
-Refer to Figure 9-3. Relative to a no-trade situation, which of the following comes with trade?
A) Consumer surplus increases by $1,800 and producer surplus increases by $1,600.
B) Consumer surplus decreases by $1,000 and producer surplus increases by $1,500.
C) Consumer surplus decreases by $1,000 and producer surplus increases by $1,750.
D) Total surplus increases by $400.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-10. The figure applies to Mexico and the good is rifles. 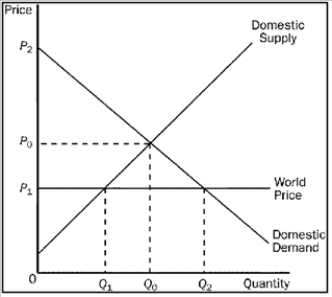 -Refer to Figure 9-10. Mexico's gains from trade are represented by the area that is bounded by the points
-Refer to Figure 9-10. Mexico's gains from trade are represented by the area that is bounded by the points
A) (0, P0) , (Q0, P0) , (Q2, P1) , and (0, P1) .
B) (0, P1) , (0, P2) , (Q0, P0) , and (Q1, P1) .
C) (Q0, P0) , (Q2, P1) , and (Q1, P1) .
D) (0, P0) , (0, P2) , and (Q0, P0) .
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-5
The figure illustrates the market for tricycles in a country.  -Refer to Figure 9-5. With trade, the price of tricycles in this country is
-Refer to Figure 9-5. With trade, the price of tricycles in this country is
A) $11, with 200 tricycles produced in this country and another 320 tricycles imported.
B) $11, with 360 tricycles produced in this country and another 160 tricycles imported.
C) $19, with 200 tricycles produced in this country and another 160 tricycles imported.
D) $19, with 360 tricycles produced in this country and another 320 tricycles imported.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 9-2
-For a small country called Boxland, the equation of the domestic demand curve for cardboard is 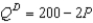 where
where 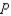
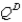 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded, in tons, and represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
-For Boxland, the equation of the domestic supply curve for cardboard is
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded, in tons, and represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
-For Boxland, the equation of the domestic supply curve for cardboard is 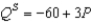 where
where 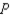
 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied, in tons, and again represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
-Refer to Scenario 9-2. Suppose the world price of cardboard is $60. Then, relative to the no-trade situation, international trade in cardboard produces which of the following results for Boxland?
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied, in tons, and again represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
-Refer to Scenario 9-2. Suppose the world price of cardboard is $60. Then, relative to the no-trade situation, international trade in cardboard produces which of the following results for Boxland?
A) It decreases consumer surplus, increases producer surplus, and decreases total surplus.
B) It decreases consumer surplus, increases producer surplus, and increases total surplus.
C) It decreases consumer surplus, decreases producer surplus, and decreases total surplus.
D) It increases consumer surplus, increases producer surplus, and increases total surplus.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a commonly-advanced argument for trade restrictions?
A) the jobs argument
B) the national-security argument
C) the infant-industry argument
D) the efficiency argument
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 261 - 280 of 492
Related Exams