B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From time to time, the demand for workers has risen in one region of the United States and fallen in another. This illustrates
A) frictional unemployment created by efficiency wages.
B) structural unemployment created by efficiency wages.
C) frictional unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
D) structural unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Table 10-5
2010 Labor Data for Tajnia
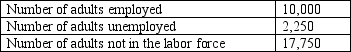 -Refer to Table 10-5. The unemployment rate of Tajnia in 2010 is about 7.5 percent.
-Refer to Table 10-5. The unemployment rate of Tajnia in 2010 is about 7.5 percent.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who is included in the labor force by the Bureau of Labor Statistics?
A) Juan, who works most of the week in a steel factory
B) Molly, who is on temporary layoff
C) Charlie, who does not have a job, but is looking for work
D) All of the above are included in the labor force.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jason works part-time as a babysitter. The Bureau of Labor Statistics counts Jason as
A) unemployed and in the labor force.
B) unemployed and not in the labor force.
C) employed and in the labor force.
D) employed and not in the labor force.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If unions were formed in more industries, the supply of labor in other industries would
A) increase, causing employment in other industries to rise.
B) increase, causing employment in other industries to fall.
C) decrease, causing employment in other industries to rise.
D) decrease, causing employment in other industries to fall.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm may pay efficiency wages in an attempt to
A) reduce incentives to shirk.
B) reduce turnover.
C) attract a well-qualified pool of applicants.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Frictional unemployment can be the consequence of
A) workers leaving existing jobs to find ones they like better.
B) one industry declining while another is growing.
C) changes in the working conditions offered by competing firms.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Some adults who were not working are included in the Bureau of Labor Statistics' "employed" category.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the wage is above the equilibrium level,
A) the labor market is functioning more efficiently than it otherwise would function.
B) there is a shortage of labor.
C) the quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity of labor demanded.
D) job search is the primary explanation for the unemployment that is observed.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Evidence from research studies by economists
A) shows that increased unemployment benefits decrease the job search efforts of the unemployed.
B) shows that increased unemployment benefits have virtually no effect on the job search efforts of the unemployed.
C) shows that increased unemployment benefits increase the job search efforts of the unemployed.
D) is conflicting on what increased unemployment benefits do to the job search efforts of the unemployed.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bureau of Labor Statistics places people in the "employed" category if they
A) are temporarily absent from their jobs.
B) are self-employed.
C) work without pay in a family member's business.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Measuring unemployment is the job of the
A) Congressional Budget Office.
B) Department of Commerce.
C) Council of Economic Advisers.
D) Bureau of Labor Statistics.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unions
A) do not affect the natural rate of unemployment.
B) lower the wages of unionized workers.
C) raise the profits of unionized firms.
D) lower the wages of workers in industries without unions.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most spells of unemployment are
A) long, and most unemployment observed at any given time is long term.
B) long, but most unemployment observed at any given time is short term.
C) short, but most unemployment observed at any given time is long term.
D) short, and most unemployment observed at any given time is short term.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is only among the least skilled and least experienced members of the labor force that minimum-wage laws cause unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unemployment that results because it takes time for workers to search for the jobs that best suit their tastes and skills is called
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) structural unemployment.
D) frictional unemployment.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Advocates of government-run employment agencies and public training programs believe they make job search more efficient.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sirius has just finished high school and started looking for his first job, but has not yet found one. Other things the same, the unemployment rate
A) and the labor-force participation rate both increase.
B) increases and the labor-force participation rate is unaffected.
C) is unaffected and the labor-force participation rate increases.
D) and the labor-force participation rate are both unaffected.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not among the four industries with the largest employment in the United States today?
A) lumber
B) aircraft
C) communications
D) electrical components
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 381 - 400 of 562
Related Exams