A) my enjoyment of the national defense does not diminish your enjoyment of the national defense of the United States.
B) my enjoyment of the national defense does diminish your enjoyment of the national defense of the United States.
C) once the nation is defended, it is impossible to prevent any single person from enjoying the benefit of this defense.
D) once the nation is defended, it is possible to prevent any single person from enjoying the benefit of this defense.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has determined that the probability of a worker dying from exposure to a hazardous chemical used in the production of fertilizer is 0.008. The cost of imposing a regulation that would ban the chemical is $32 million. If the value of a human life is equal to $10 million, how many people must the policy affect in order for the benefits to exceed the costs?
A) 256
B) 401
C) 3201
D) 4001
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 11-3
This table describes the police protection demands for three equal sized groups of people in Safetyville. The second, third, and fourth columns show the number of person-hours of police protection per day that a group will demand for a given price (the first column) .
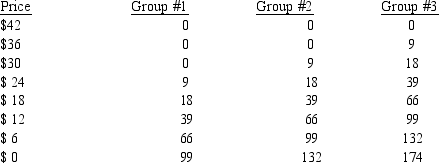 -Refer to Table 11-3. What is the value of the 39th unit of police protection in Safetyville?
-Refer to Table 11-3. What is the value of the 39th unit of police protection in Safetyville?
A) $24
B) $42
C) $54
D) $72
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A free rider is a person who
A) will only purchase a product on sale.
B) receives the benefit of a good but avoids paying for it.
C) can produce a good at no cost.
D) rides public transit regularly.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Variable tolls on roads
A) are politically unpopular because people do not like the idea of paying for a good that they used to consume without paying for it directly.
B) rise when traffic volume increases to ensure the speed on the road is kept high.
C) are an effective way of correcting the common resource problem on roads.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Concerts in arenas are not excludable because it is virtually impossible to prevent someone from seeing the show.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For most goods in an economy, the primary signal that guides the decisions of buyers and sellers is
A) advertising.
B) quality.
C) reputation.
D) price.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If good x is available free of charge, then
A) good x must be provided by nature.
B) good x must be provided by the government.
C) the private market cannot ensure an efficient allocation of resources in the market for good x.
D) government policy is incapable of increasing total surplus in the market for good x.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A city street is
A) always a public good, whether or not it is congested.
B) a public good when it is congested, but it is a common resource when it is not congested.
C) a common resource when it is congested, but it is a public good when it is not congested.
D) always a common resource, whether or not it is congested.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Tragedy of the Commons
A) occurs most often with public goods.
B) is only applicable to shared grazing rights among sheep herders.
C) is eliminated when property rights are assigned to individuals.
D) occurs when social incentives are in line with private incentives.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 11-5
A small island off the coast of Cape Cod contains two restaurants and two retail stores. Tourists need to take a ferry boat to reach the island, but with a recent slowdown in the economy, tourists are less willing to pay for the boat ride to visit the island. The owners of the restaurants and stores on the island - Restaurants 1 and 2, and Stores A and B - think that if tourists could ride the ferry for free, they would be happy to visit the island, eat and shop. The business owners are considering contributing to a pool of money that will be used to pay for roundtrip ferry service each day. The table represents their willingness to pay, that is, the maximum amount that each business owner is willing to contribute, per day, to pay for each ferry trip.
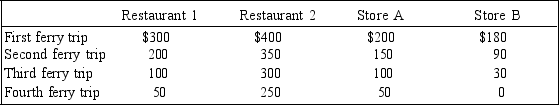 -Refer to Table 11-5. Suppose the cost to run the ferry for each roundtrip is $1,000 per day and the 4 business owners have agreed to split the costs of the ferry trips equally. How many ferry trips would the owner of Store A prefer to have?
-Refer to Table 11-5. Suppose the cost to run the ferry for each roundtrip is $1,000 per day and the 4 business owners have agreed to split the costs of the ferry trips equally. How many ferry trips would the owner of Store A prefer to have?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Private goods and club goods have in common that they are excludable, but are different in that private goods are rival while club goods are not rival in consumption.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Four friends decide to meet at a Chinese restaurant for dinner. They decide that each person will order an item off the menu, and they will share all dishes. They will split the cost of the final bill evenly among each of the people at the table. A Tragedy of the Commons problem is likely for each of the following reasons except
A) each person has an incentive to eat as fast as possible since their individual rate of consumption will not affect their individual cost.
B) there is an externality associated with eating the food on the table.
C) when one person eats, he may not take into account how his choice affects his friends.
D) each dish would be both excludable and rival in consumption.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The pollution market failure is an example of the free rider problem.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 11-1
Consider the town of Springfield with only three residents, Sophia, Amber, and Cedric. The three residents are trying to determine how large, in acres, they should build the public park. The table below shows each resident's willingness to pay for each acre of the park.
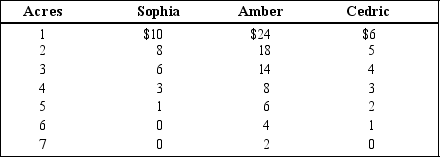 -Refer to Table 11-1. Suppose the cost to build the park is $9 per acre and that the residents have agreed to split the cost of building the park equally. If the residents vote to determine the size of park to build, basing their decision solely on their own willingness to pay (and trying to maximize their own surplus) , what is the largest park size for which the majority of residents would vote "yes?"
-Refer to Table 11-1. Suppose the cost to build the park is $9 per acre and that the residents have agreed to split the cost of building the park equally. If the residents vote to determine the size of park to build, basing their decision solely on their own willingness to pay (and trying to maximize their own surplus) , what is the largest park size for which the majority of residents would vote "yes?"
A) 1 acre
B) 2 acres
C) 3 acres
D) 4 acres
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 11-5
A small island off the coast of Cape Cod contains two restaurants and two retail stores. Tourists need to take a ferry boat to reach the island, but with a recent slowdown in the economy, tourists are less willing to pay for the boat ride to visit the island. The owners of the restaurants and stores on the island - Restaurants 1 and 2, and Stores A and B - think that if tourists could ride the ferry for free, they would be happy to visit the island, eat and shop. The business owners are considering contributing to a pool of money that will be used to pay for roundtrip ferry service each day. The table represents their willingness to pay, that is, the maximum amount that each business owner is willing to contribute, per day, to pay for each ferry trip.
 -Refer to Table 11-5. Suppose the cost to run the ferry for each roundtrip is $500. How many ferry trips should there be to maximize the total surplus of the four business owners?
-Refer to Table 11-5. Suppose the cost to run the ferry for each roundtrip is $500. How many ferry trips should there be to maximize the total surplus of the four business owners?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A free rider problem arises when
A) there are very few beneficiaries and exclusion of any one of them is possible.
B) there are many beneficiaries and exclusion of any one of them is possible.
C) there are many beneficiaries and exclusion of any one of them is impossible.
D) there are very few beneficiaries and they all try to use the good simultaneously.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a road is congested, then use of that road by an additional person would lead to a
A) negative externality.
B) positive externality.
C) Pigovian externality.
D) free-rider problem with rush hour drivers stuck in traffid.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
National Public Radio would be considered a club good.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following problems: overcrowded public highways, overfishing in the ocean, polluted air, and the near- extinction of the wild rhinoceros. What do these problems have in common?
A) Private markets could easily solve them if governments left the markets alone.
B) They would all go away if the government sponsored an intensive public-information campaign.
C) They are all the result of a failure to establish clear property rights over something of value.
D) They are all the result of a failure of corrective taxes.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 433
Related Exams