A) 2 bolts and 2 nails and Azerbaijan gained 2 bolts and 18 nails.
B) 4 bolts and 2 nails and Azerbaijan gained 2 bolts and 14 nails.
C) 14 bolts and 38 nails and Azerbaijan gained 16 bolts and 42 nails.
D) 16 bolts and 38 nails and Azerbaijan gained 16 bolts and 38 nails.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 3-19 Summary of the Gains from Trade
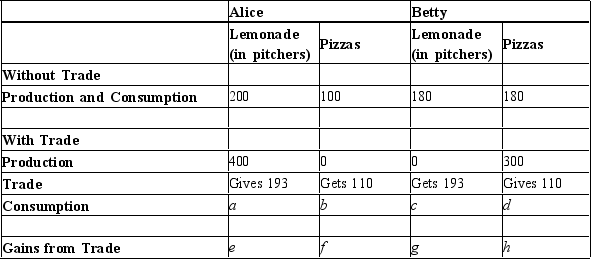 -Refer to Table 3-19. The values in the table represent the amounts of lemonade and pizzas that Alice and Betty can produce in one week without and with specialization and trade. What are Alice and Betty's gains from specialization and trade?
-Refer to Table 3-19. The values in the table represent the amounts of lemonade and pizzas that Alice and Betty can produce in one week without and with specialization and trade. What are Alice and Betty's gains from specialization and trade?
A) Alice gains 7 pitchers of lemonade and 10 pizzas, while Betty gains 13 pitchers of lemonade and 10 pizzas.
B) Alice gains 200 pitchers of lemonade and 100 pizzas, while Betty gains 180 pitchers of lemonade and 180 pizzas.
C) Alice gains 207 pitchers of lemonade and 110 pizzas, while Betty gains 193 pitchers of lemonade and 190 pizzas.
D) Alice gains 400 pitchers of lemonade and 0 pizzas, while Betty gains 0 pitchers of lemonade and 300 pizzas.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 3-23
Assume that the farmer and the rancher can switch between producing pork and producing tomatoes at a constant rate.
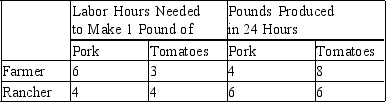 -Refer to Table 3-23. The farmer should specialize in the production of
-Refer to Table 3-23. The farmer should specialize in the production of
A) pork and the rancher should specialize in the production of tomatoes.
B) tomatoes and the rancher should specialize in the production of pork.
C) both goods and the rancher should specialize in the production of neither good.
D) neither good and the rancher should specialize in the production of both goods.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 3-35
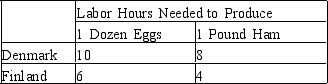 -Refer to Table 3-35. At which of the following prices, if any, could both Denmark and Finland gain from trade?
-Refer to Table 3-35. At which of the following prices, if any, could both Denmark and Finland gain from trade?
A) 2/3 pounds of ham per dozen eggs.
B) 1 pound of ham per dozen eggs.
C) 1.4 pounds of ham per dozen eggs.
D) None of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Jake can complete an oil change in 45 minutes and he can write a poem in 90 minutes. Ming-la can complete an oil change in 30 minutes and she can write a poem in 90 minutes. Jake's opportunity cost of writing a poem is lower than Ming-la's opportunity cost of writing a poem.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 3-24
Assume that England and Spain can switch between producing cheese and producing bread at a constant rate.
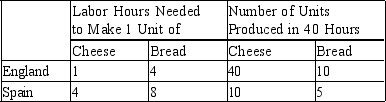 -Refer to Table 3-24. The opportunity cost of 1 unit of bread for England is
-Refer to Table 3-24. The opportunity cost of 1 unit of bread for England is
A) 1/4 unit of cheese.
B) 1/4 hour of labor.
C) 4 units of cheese.
D) 4 hours of labor.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 3-25
Chile's Production Possibilities Frontier Colombia's Production Possibilities Frontier 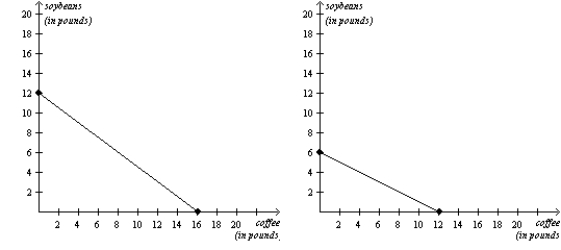 -Refer to Figure 3-25. Colombia should specialize in the production of
-Refer to Figure 3-25. Colombia should specialize in the production of
A) coffee and import soybeans.
B) soybeans and import coffee.
C) both goods and import neither good.
D) neither good and import both goods.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 3-24
Assume that England and Spain can switch between producing cheese and producing bread at a constant rate.
 -Refer to Table 3-24. England has a comparative advantage in the production of
-Refer to Table 3-24. England has a comparative advantage in the production of
A) cheese and Spain has a comparative advantage in the production of bread.
B) bread and Spain has a comparative advantage in the production of cheese.
C) both goods and Spain has a comparative advantage in the production of neither good.
D) neither good and Spain has a comparative advantage in the production of both goods.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 3-9
Uzbekistan's Production Possibilities Frontier Azerbaijan's Production Possibilities Frontier 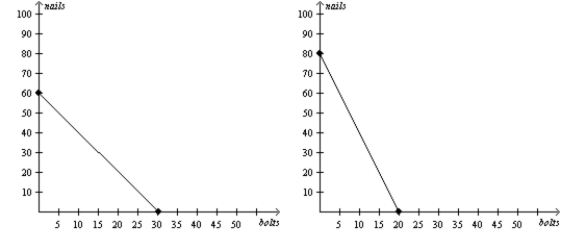 -Refer to Figure 3-9. If the production possibilities frontiers shown are each for two days of production, then which of the following combinations of bolts and nails could Uzbekistan and Azerbaijan together not make in a given 2-day production period?
-Refer to Figure 3-9. If the production possibilities frontiers shown are each for two days of production, then which of the following combinations of bolts and nails could Uzbekistan and Azerbaijan together not make in a given 2-day production period?
A) 9 bolts and 122 nails
B) 21 bolts and 98 nails
C) 36 bolts and 56 nails
D) 47 bolts and 18 nails
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 3-26
Assume that Japan and Korea can switch between producing cars and producing airplanes at a constant rate.
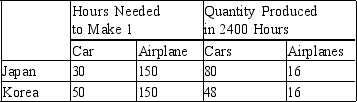 -Refer to Table 3-26. Suppose Korea decides to increase its production of cars by 18. What is the opportunity cost of this decision?
-Refer to Table 3-26. Suppose Korea decides to increase its production of cars by 18. What is the opportunity cost of this decision?
A) 3 airplanes
B) 6 airplanes
C) 16 airplanes
D) 150 airplanes
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A production possibilities frontier is bowed outward when
A) the more resources the economy uses to produce one good, the fewer resources it has available to produce the other good.
B) an economy is self-sufficient instead of interdependent and engaged in trade.
C) the rate of tradeoff between the two goods being produced is constant.
D) the rate of tradeoff between the two goods being produced depends on how much of each good is being produced.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 3-10
Alice and Betty's Production Possibilities in one 8hour day.
Alice's Production Possibilities Frontier Betty's Production Possibilities Frontier
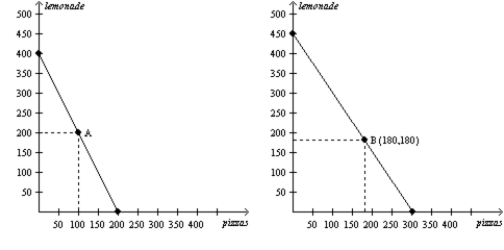 -Refer to Figure 3-10. If Alice produces only lemonade, she can produce
-Refer to Figure 3-10. If Alice produces only lemonade, she can produce
A) 200 pitchers per day.
B) 300 pitchers per day.
C) 400 pitchers per day.
D) 450 pitchers per day.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 3-30
Assume that Falda and Varick can switch between producing wheat and producing cloth at a constant rate.
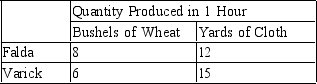 -Refer to Table 3-30. Falda has an absolute advantage in the production of
-Refer to Table 3-30. Falda has an absolute advantage in the production of
A) wheat.
B) cloth.
C) both goods.
D) neither good.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 3-35
 -Refer to Table 3-35. Which good(s) does Finland have an absolute advantage producing?
-Refer to Table 3-35. Which good(s) does Finland have an absolute advantage producing?
A) both eggs and ham.
B) eggs but not ham.
C) ham but not eggs.
D) neither ham nor eggs.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 3-19
Chile's Production Possibilities Frontier Colombia's Production Possibilities Frontier 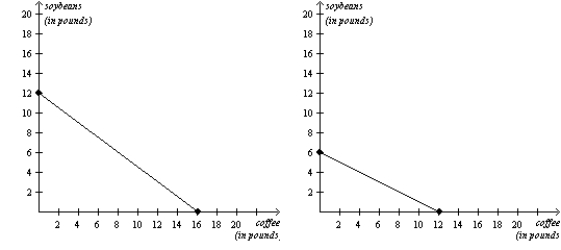 -Refer to Figure 3-19. Chile has a comparative advantage in the production of
-Refer to Figure 3-19. Chile has a comparative advantage in the production of
A) coffee and Colombia has a comparative advantage in the production of soybeans.
B) soybeans and Colombia has a comparative advantage in the production of coffee.
C) both goods and Colombia has a comparative advantage in the production of neither good.
D) neither good and Colombia has a comparative advantage in the production of both goods.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Opportunity cost measures the trade-off between two goods that each producer faces.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose that in one hour Dewey can produce either 10 bushels of corn or 20 yards of cloth. Dewey's opportunity cost of producing one bushel of corn is 1/2 yard of cloth.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 3-4
Lisa's Production Possibilities Frontier Bryce's Production Possibilities Frontier
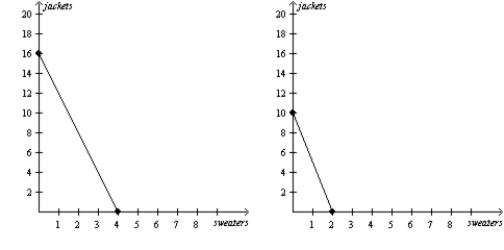 -Refer to Figure 3-4. If the production possibilities frontiers shown are each for one year of production, then which of the following combinations of sweaters and jackets could Lisa and Bryce together not produce in a given year?
-Refer to Figure 3-4. If the production possibilities frontiers shown are each for one year of production, then which of the following combinations of sweaters and jackets could Lisa and Bryce together not produce in a given year?
A) 1 sweater and 21 jackets
B) 2 sweaters and 20 jackets
C) 3 sweaters and 12 jackets
D) 5 sweaters and 4 jackets
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 3-18
Bintu's Production Possibilities Frontier Juba's Production Possibilities Frontier 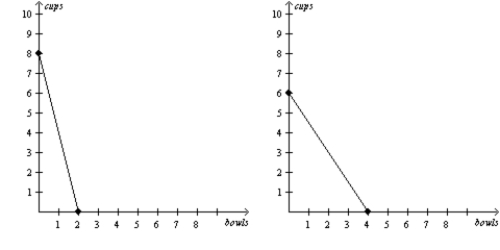 -Refer to Figure 3-18. The opportunity cost of 1 cup for Juba is
-Refer to Figure 3-18. The opportunity cost of 1 cup for Juba is
A) 1/6 bowl.
B) 2/3 bowl.
C) 3/2 bowls.
D) 6 bowls.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 3-12
Barb and Jim run a business that sets up and tests computers. Assume that Barb and Jim can switch between setting up and testing computers at a constant rate. The following table applies.
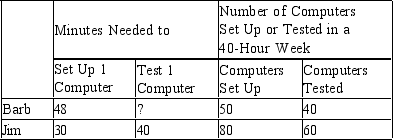 -Refer to Table 3-12. Which of the following points would not be on Jim's production possibilities frontier, based on a 40-hour week?
-Refer to Table 3-12. Which of the following points would not be on Jim's production possibilities frontier, based on a 40-hour week?
A) (0 computers set up, 60 computers tested)
B) (40 computers set up, 30 computers tested)
C) (60 computers set up, 12 computers tested)
D) (72 computers set up, 6 computers tested)
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 527
Related Exams