A) increase by $250 billion.
B) increase by $333 billion.
C) increase by $360 billion.
D) None of the above are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary argument against active monetary and fiscal policy is that
A) attempts to stabilize the economy do not constitute a proper role for government in a democratic society.
B) these policies affect the economy with a long lag.
C) these policies affect the economy too quickly and with too much impact.
D) history demonstrates that interest rates respond unpredictably to active policies, leading to unpredictable effects on income.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Critics of stabilization policy argue that
A) there is a lag between the time policy is passed and the time policy has an impact on the economy.
B) the impact of policy may last longer than the problem it was designed to offset.
C) policy can be a source of, instead of a cure for, economic fluctuations.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct for the long run?
A) Output is determined by the amount of capital, labor, and technology; the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply and demand for money; the price level adjusts to balance the supply and demand for loanable funds.
B) Output is determined by the amount of capital, labor, and technology; the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply and demand for loanable funds; the price level adjusts to balance the supply and demand for money.
C) Output is determined by the amount of capital, labor, and technology; the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply and demand for loanable funds; the price level is relatively slow to adjust.
D) Output responds to the aggregate demand for goods and services; the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply and demand for loanable funds; the price level adjusts to balance the supply and demand for money.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the stock market booms, then
A) aggregate demand increases, which the Fed could offset by increasing the money supply.
B) aggregate supply increases, which the Fed could offset by increasing the money supply.
C) aggregate demand increases, which the Fed could offset by decreasing the money supply.
D) aggregate supply increases, which the Fed could offset by decreasing the money supply.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Federal Reserve increases the money supply, then initially there is a
A) shortage in the money market, so people will want to sell bonds.
B) shortage in the money market, so people will want to buy bonds.
C) surplus in the money market, so people will want to sell bonds.
D) surplus in the money market, so people will want to buy bonds.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Automatic stabilizers
A) increase the problems that lags cause in using fiscal policy as a stabilization tool.
B) are changes in taxes or government spending that increase aggregate demand without requiring policy makers to act when the economy goes into recession.
C) are changes in taxes or government spending that policy makers quickly agree to when the economy goes into recession.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary policy affects the economy with a long lag, in part because
A) proposals to change monetary policy must go through both the House and Senate before being sent to the president.
B) monetary policy works through changes in interest rates, and the Fed does not have the ability to change interest rates quickly.
C) changes in interest rates primarily influence consumption spending, and households make consumption plans far in advance.
D) changes in interest rates primarily influence investment spending, and firms make investment plans far in advance.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Kennedy tax cut of 1964 included an investment tax credit that was designed to
A) increase aggregate demand in the short run and aggregate supply in the long run.
B) increase aggregate supply in the short run and aggregate demand in the long run.
C) only increase aggregate supply in the long run.
D) only increase aggregate demand in the short run.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose there were a large increase in net exports. If the Fed wanted to stabilize output, it could
A) buy bonds to increase the money supply.
B) buy bonds to decrease the money supply.
C) sell bonds to increase the money supply.
D) sell bonds to decrease the money supply.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The logic of the multiplier effect applies
A) only to changes in government spending.
B) to any change in spending on any component of GDP.
C) only to changes in the money supply.
D) only when the crowding-out effect is sufficiently strong.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If expected inflation is constant, then when the nominal interest rate falls, the real interest rate
A) falls by more than the change in the nominal interest rate.
B) falls by the change in the nominal interest rate.
C) rises by the change in the nominal interest rate.
D) rises by more than the change in the nominal interest rate.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following cases would the quantity of money demanded be largest?
A) r = 0.03, P = 1.2
B) r = 0.03, P = 1.3
C) r = 0.04, P = 1.2
D) r = 0.05, P = 0.9
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the interest rate increases, the opportunity cost of holding money
A) increases, so the quantity of money demanded increases.
B) increases, so the quantity of money demanded decreases.
C) decreases, so the quantity of money demanded increases.
D) decreases, so the quantity of money demanded decreases.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-4. On the figure, MS represents money supply and MD represents money demand. 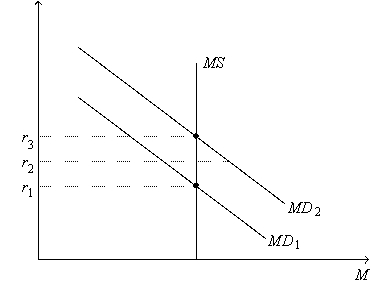 -Refer to Figure 21-4. Which of the following events could explain a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate from r3 to r1?
-Refer to Figure 21-4. Which of the following events could explain a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate from r3 to r1?
A) a decrease in the price level
B) a decrease in the number of firms building new factories and buying new equipment
C) an increase in the price level
D) an increase in the number of firms building new factories and buying new equipment
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume there is a multiplier effect, some crowding out, and no accelerator effect. An increase in government expenditures changes aggregate demand more,
A) the smaller the MPC and the stronger the influence of income on money demand.
B) the smaller the MPC and the weaker the influence of income on money demand.
C) the larger the MPC and the stronger the influence of income on money demand.
D) the larger the MPC and the weaker the influence of income on money demand.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People are likely to want to hold more money if the interest rate
A) increases, making the opportunity cost of holding money rise.
B) increases, making the opportunity cost of holding money fall.
C) decreases, making the opportunity cost of holding money rise.
D) decreases, making the opportunity cost of holding money fall.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the MPC is 0.75. Assume there is a multiplier effect and that the total crowding-out effect is $6 billion. An increase in government purchases of $10 billion will shift aggregate demand to the
A) left by $24 billion.
B) left by $36 billion.
C) right by $34 billion.
D) right by $36 billion.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
According to the theory of liquidity preference, the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply of, and demand for, loanable funds.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To decrease the interest rate the Federal Reserve could
A) buy bonds. The fall in the interest rate would increase investment spending.
B) buy bonds. The fall in the interest rate would decrease investment spending.
C) sell bonds. The fall in the interest rate would increase investment spending
D) sell bonds. The fall in the interest rate would decrease investment spending.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 416
Related Exams