A) above the equilibrium price, causing a shortage.
B) above the equilibrium price, causing a surplus.
C) below the equilibrium price, causing a shortage.
D) below the equilibrium price, causing a surplus.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A binding minimum wage in a competitive labor market creates unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 6-11. On the graph below, the shift of the supply curve from S₁ to S₂ represents the imposition of a tax on a good. On the axes, Q represents the quantity of the good and P represents the price.
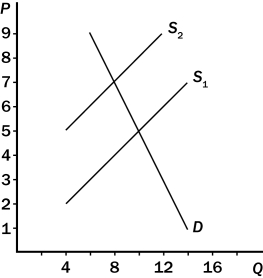 -Consider Figure 6-11.As a result of the tax,
-Consider Figure 6-11.As a result of the tax,
A) the price paid by buyers rises from $5 to $7.
B) the price received by sellers (after paying the tax) falls from $5 to $3.
C) the government collects $30 in tax revenue.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If we were to construct an elasticity of teenage employment with respect to the minimum wage,the value of that elasticity would be about
A) -1.0 to -0.4.
B) -0.3 to -0.1.
C) 0.2 to 0.7.
D) 0.5 to 1.0.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the government passes a law requiring buyers of a good to send one dollar to the government for every unit of the good they buy,
A) the supply curve for the good shifts to the right.
B) the demand curve for the good shifts to the left.
C) more than 50 percent of the burden of the tax falls on buyers.
D) the government collects less tax revenue than it would collect if the sellers of the good were required to send one dollar to the government for every unit of the good they sell.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a price ceiling is not binding,it will have no effect on the market.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 6-13
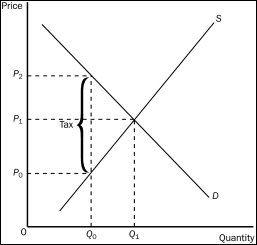 -Refer to Figure 6-13.The effective price that will be paid by buyers after the tax is
-Refer to Figure 6-13.The effective price that will be paid by buyers after the tax is
A) P₀.
B) P₁.
C) P₂.
D) impossible to determine.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) A price ceiling is not binding when the price ceiling is set above the equilibrium price.
B) A price floor is not binding when the price floor is set below the equilibrium price.
C) A binding price ceiling causes a shortage and a binding price floor causes a surplus.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The presence of price controls in a market usually is an indication that
A) an insufficient quantity of a good or service was being produced in that market to meet the public's need.
B) the usual forces of supply and demand were not able to establish an equilibrium price in that market.
C) policymakers believed that the price that prevailed in that market in the absence of price controls was unfair to buyers or sellers.
D) policymakers correctly believed that, in that market, price controls would generate no inequities of their own.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When policymakers set prices by legal decree,they
A) are usually following the advice of mainstream economists.
B) are usually improving the organization of economic activity.
C) are obscuring the signals that normally guide the allocation of society's resources.
D) are demonstrating a willingness to sacrifice equity for the sake of a gain in efficiency.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a correct statement about the labor market?
A) Workers determine the supply of labor, and firms determine the demand for labor.
B) Workers determine the demand for labor, and firms determine the supply of labor.
C) Workers determine the supply of labor, and government determines the demand for labor.
D) The forces of supply and demand, while present in the labor market, have nothing to balance in that market.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a price ceiling is below equilibrium price,the quantity demanded will exceed the quantity supplied.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 6-1
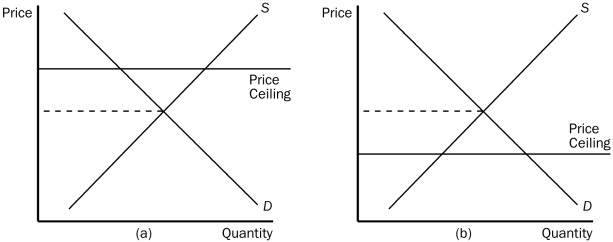 -Refer to Figure 6-1.In which panel(s) of the figure would there be a shortage of the good at the ceiling price?
-Refer to Figure 6-1.In which panel(s) of the figure would there be a shortage of the good at the ceiling price?
A) panel (a) but not panel (b)
B) panel (b) but not panel (a)
C) panel (a) and panel (b)
D) neither panel (a) nor panel (b)
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Earned Income Tax Credit is an example of
A) a minimum-wage policy.
B) a price ceiling.
C) a wage subsidy.
D) a rent subsidy.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Since half of the FICA tax is paid by firms,and the other half is paid by workers,the burden of the tax must fall equally on firms and workers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of a price floor is
A) the regulation of gasoline prices in the U.S.in the 1970s.
B) rent control.
C) the minimum wage.
D) any restriction on price that leads to a shortage.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 6-10
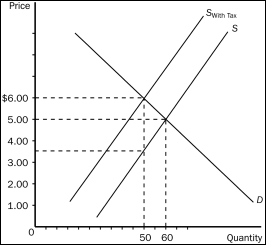 -Refer to Figure 6-10.The effective price sellers receive after the tax is imposed is
-Refer to Figure 6-10.The effective price sellers receive after the tax is imposed is
A) $1.00.
B) $3.50.
C) $5.00.
D) $6.00.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 6-5
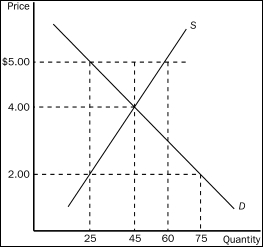 -Refer to Figure 6-5.If the government imposes a price ceiling of $2.00 in this market,the result is a
-Refer to Figure 6-5.If the government imposes a price ceiling of $2.00 in this market,the result is a
A) surplus of 30 units of the good.
B) shortage of 20 units of the good.
C) shortage of 30 units of the good.
D) shortage of 50 units of the good.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rationing by long lines is
A) inefficient, because it wastes buyers' time.
B) efficient, because those who are willing to wait the longest get the goods.
C) the only way scarce goods can be rationed.
D) only necessary if price ceilings are not binding.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a binding price ceiling were imposed in the computer market,
A) the quantity of computers demanded would increase.
B) the quantity of computers supplied would decrease.
C) a shortage of computers would develop.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 252
Related Exams